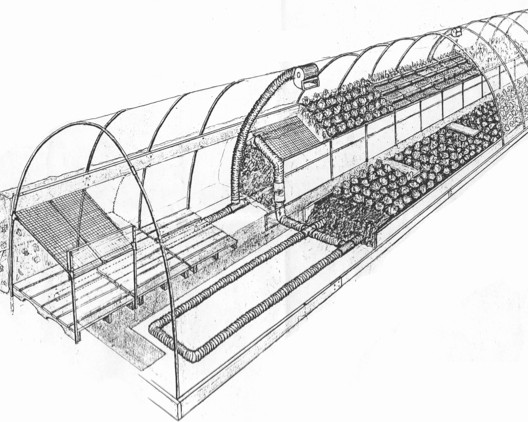
A bioshelter is a new, more complex form of greenhouse that can meet important basic human needs. Bioshelters imagine a new synthesis between people and their local ecology: an early exploration in weaving together the sun, wind, biology and architecture on behalf of humanity. The architecture protects the ecosystem inside from extremes of wind and cold, and absorbs the energy from sunlight that causes plants to grow and heats the air.
The ecosystem includes soil life, diverse plants, fish, insects, frogs, and people. Food is produced as nutrients cycle through plants and soil. Water is captured, stored, warmed and directed to crops and ponds.
Water Tubes
The Holy Grail of Thermal Mass for Solar Greenhouses
Click here for a downloadable PDF of this report by Earle Barnhart
“Alchemical processes depend on the maintenance of steady temperatures, and much experience is needed in the design of furnaces to precisely regulate the heat and draft …”
-quote from Old Alchemy
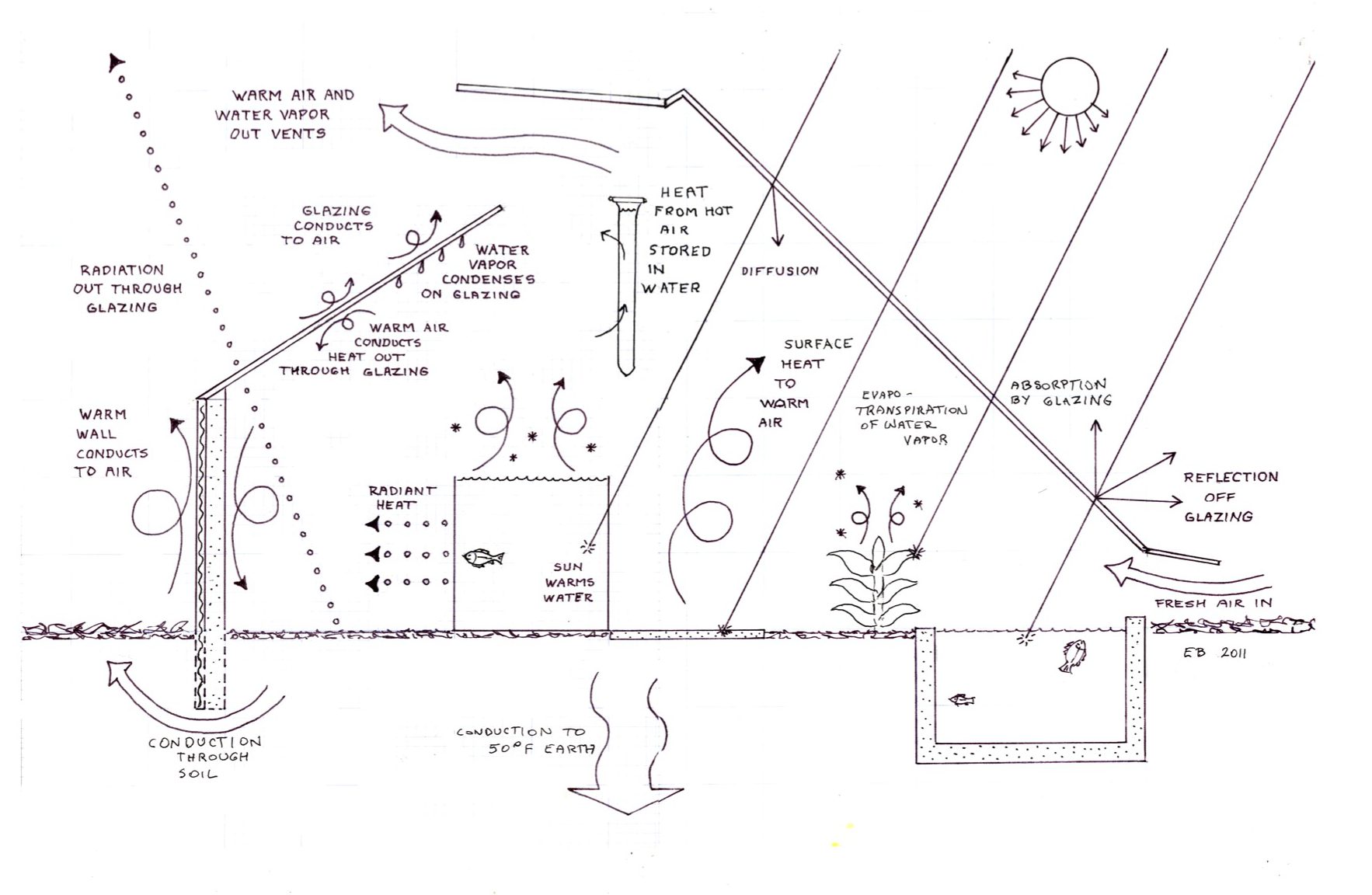
Passive solar heat storage in water tubes
These Greenway Passive Solar Heat Storage Tubes absorb and store excess heat from greenhouse air during the day and release the stored heat into the greenhouse at night. Water is the best material for heat storage, storing the most heat for its volume. Each tube, made from Teflon, is 100% transparent, letting sunlight pass on through to growing plants in the greenhouse. Heat is absorbed automatically from warm air, and is released automatically back into colder air. Water tubes are most efficient if hung high in a greenhouse where the air is warmest and above the soil and crops.
Benefits of water tubes
- Automatic: the air and heat move naturally
- Silent: no fans, no power, no fuel, no burners
- Simple: no mechanical or digital controls, so you can see them working
- More attractive than ducts
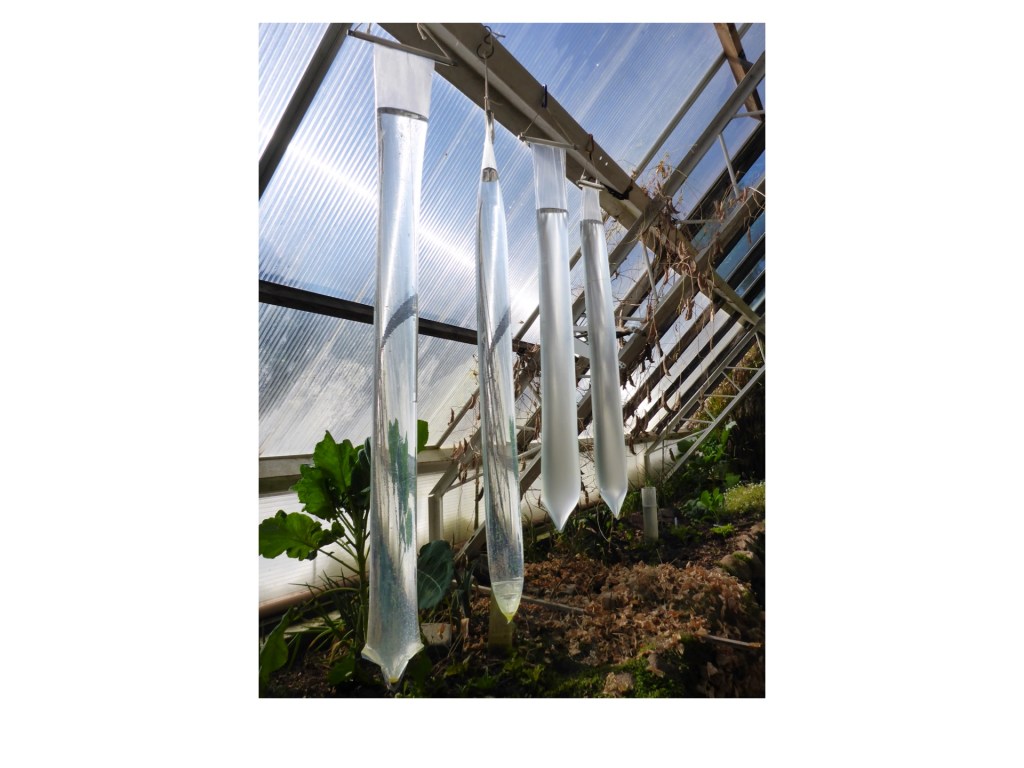

The air in a greenhouse on a sunny day will get hotter and hotter, and usually it is vented out of the greenhouse and wasted.
A transparent tube of water hanging in the greenhouse will absorb the heat from the hot air and store it as warm water. Later at night when the greenhouse cools, heat is released from the warm water and heats the greenhouse air. Water is the best material to store heat; it holds the most heat for its volume.
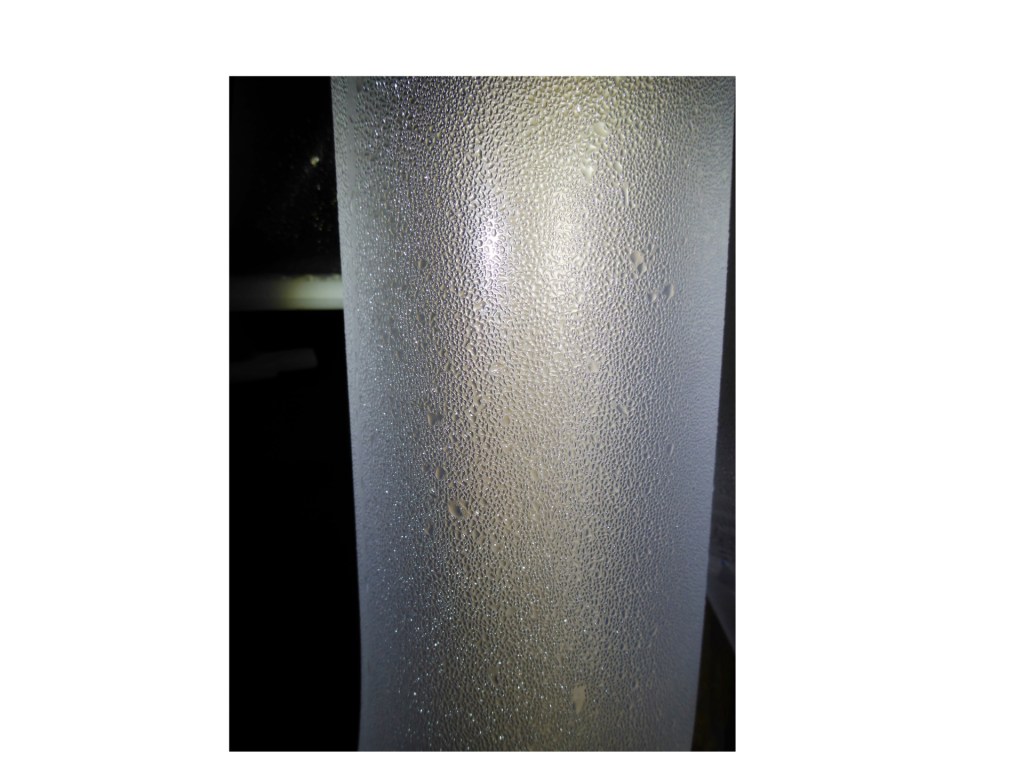
When warm moist air cools on a cold water tube, drops of condensation will form on the surface. Condensation will be visible while absorbing heat. At night, it evaporates off and the tube is clear.

During the daytime, the process works as follows:
- warm air touches tube
- heat moves into water inside
- warmest water rises to top
- cooled air sinks downward

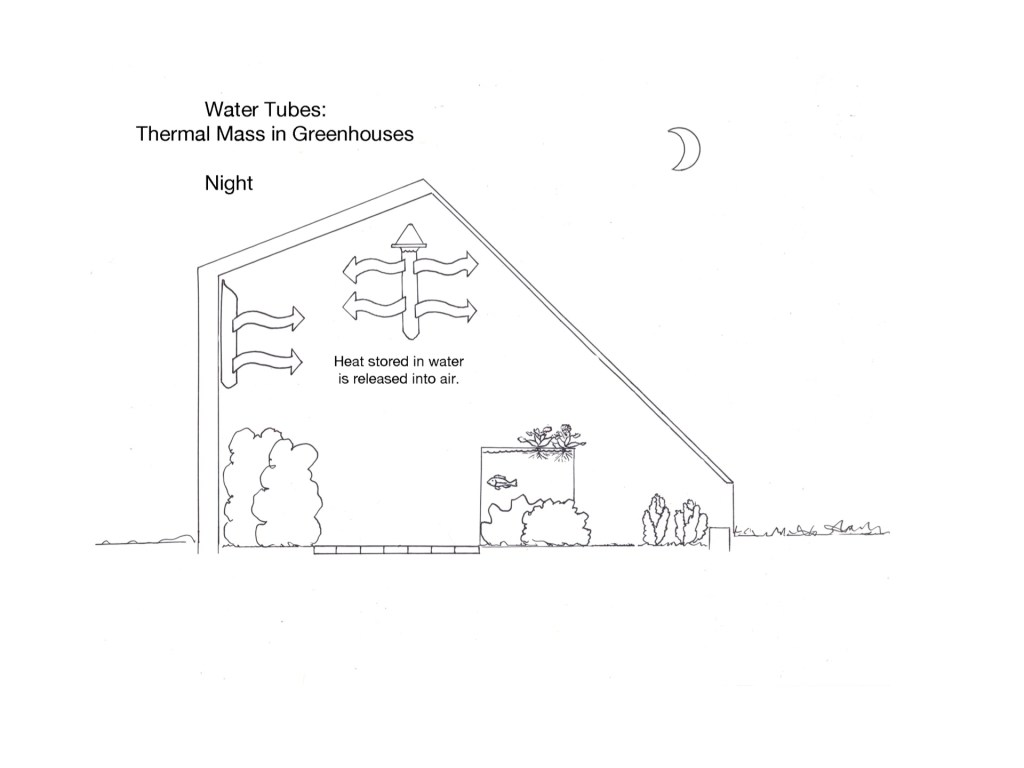
During the night, the now-warm tube radiates heat and the air touching tube becomes warm, rising upward.
Notes from personal experience
When warm moist air cools on a cold water tube, drops of condensation will form on the surface. When absorbing heat, the condensation will stay visible. When heat is released at night, it evaporates off and the tube is clear. The water at the top of the below tube is very warm and is not cooling any air.


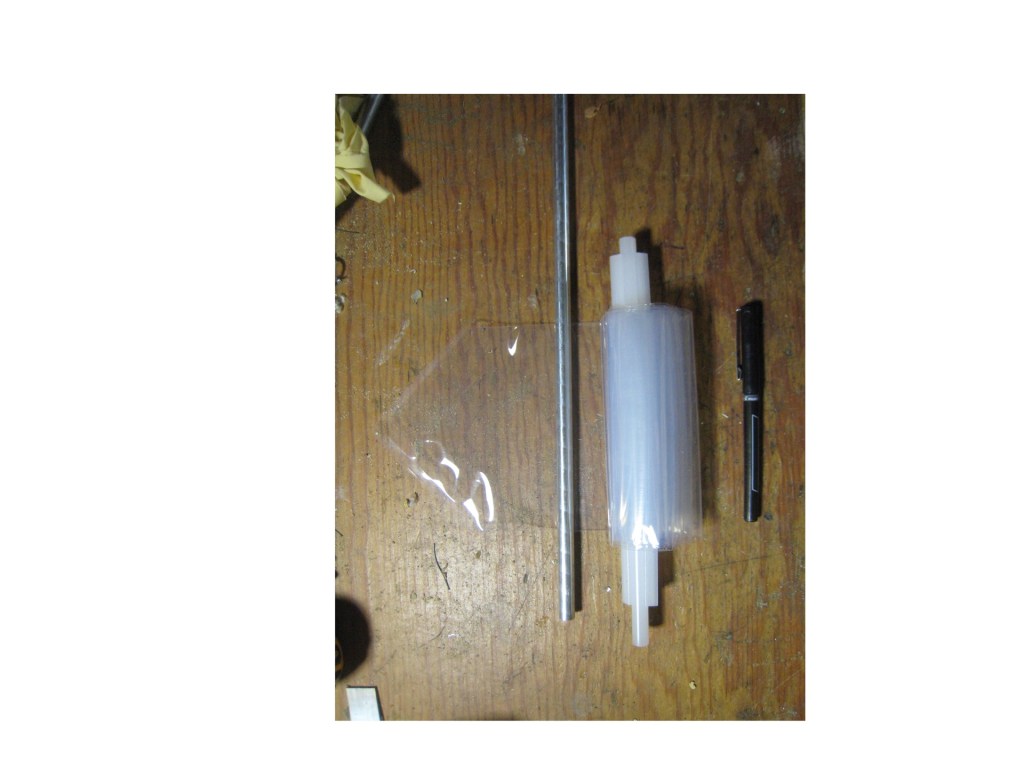
Trial and Error
Using 2 polyethylene tubes 2″ and 4″ diameter, the water tubes will fail in a year or two.
Using 2 Teflon tubes, they remained inert and clear and stable shape.
Using 2 nylon tubes, we had a catastrophic failure every 3 months with cloudy water and bulges in the bottom.
Plastic rods bend and distort; so does wood; aluminum rods are better.
We found that 4 inch diameter tubes are very heavy and hard to handle.
Sealed bottoms are necessary, simple tying and clamps will leak

Hanging in freezing air, eventually the water in a tube will freeze. Water expands about 9% in volume when frozen.
Water tubes are more effective if they are placed high in a greenhouse and distributed in many places.

Other thermal mass

Plant leaves are 95% water; the water in leaves also store heat during the day and release it at night. 
Solar fish ponds warm up 5 degrees F on a sunny day and can release heat for several sunless days while slowly cooling .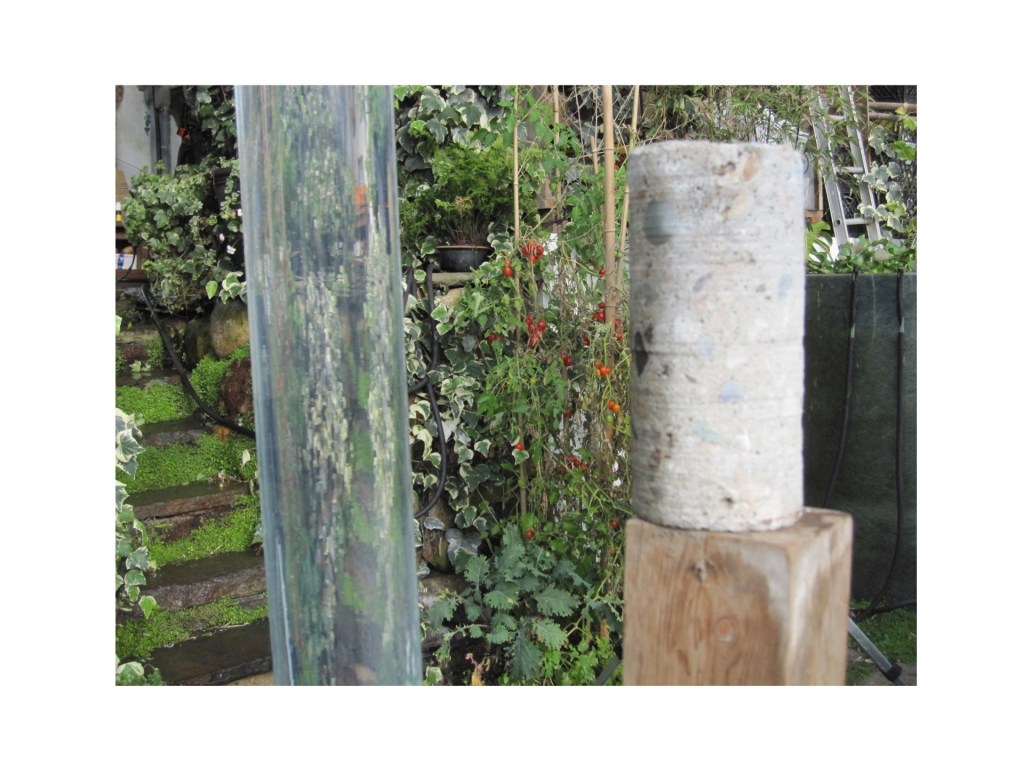 
Water stores twice as much heat as cement. 
Bottles of water work well, are cheap, and can last years.
Why Not Black?
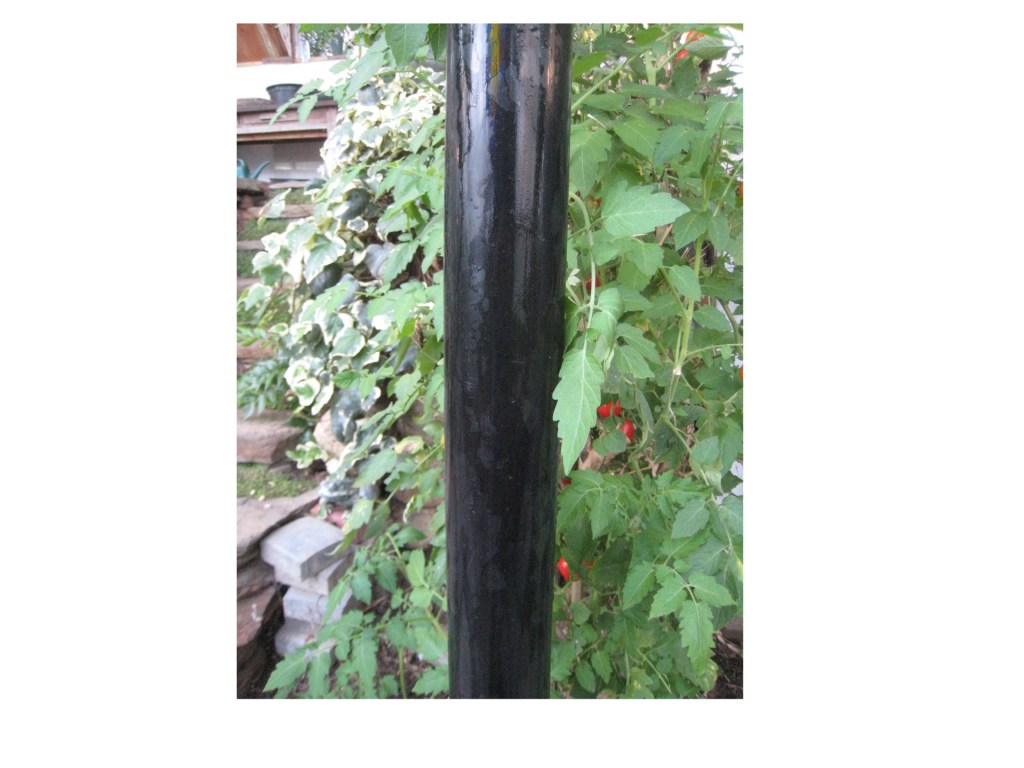

Plants in a greenhouse need the maximum amount of light possible to photosynthesize and grow.
A clear tube in front of a plant will let light go through and hit the plant. A clear tube will only only absorb heat from nearby air.
A black tube in front of a plant will absorb light, leaving less light will hit the plant. A black tube will absorb both heat from nearby air and light that strikes it, which turns into heat. A black tube will get hotter than a clear tube.
Black containers of water are useful to absorb light that will not strike a plant, such as at the north wall. On sunny days black metal drums of water can store large amounts of heat.
For people, black walls can be slightly depressing to look at and spend time near.




Leave a reply to James Berk Cancel reply